Injection molding automation means building integrated cells around injection molding machines, where robots, feeding systems, assembly units and inline quality control work together to produce parts with minimal manual intervention.
Factory automation is no longer optional in high-volume plastic manufacturing. As product lifecycles shorten and quality expectations rise, injection molding automation has become one of the most effective ways to keep capacity, quality, and unit costs under control.
At Mikropakk, we operate both partially and fully automated injection molding and assembly lines that can produce millions of plastic components per year. Below, we show what injection molding automation means in practice, how it changes workflows, and how it helps us deliver consistently high quality at scale.
How injection molding automation changes workflows
On a traditional injection molding line, operators handle many tasks around the machine: loading components, removing parts from the mold, performing visual checks, assembling components, and packaging finished products. Partially automated lines still rely heavily on manual work in these areas.
In a fully automated injection molding cell, robots and dedicated equipment carry out most of these steps. Operators focus on supervision, quality oversight, and changeovers instead of repetitive manual operations.
In a typical automated setup around an injection molding machine, robots and automation modules can perform:
- automatic feeding and orientation of molded and purchased components
- high-speed take-out of parts from the mold
- visual or other inline quality inspections of plastic parts
- pad printing and decoration with integrated quality checks
- assembly and securing of multiple plastic and non-plastic components
- comprehensive quality control of the finished product, including functional tests
- sorting and isolation of non-conforming parts
Well-designed injection molding automation not only increases output; it also reduces process variation. Robotized workflows follow the same sequence with the same timing in every cycle, which stabilises quality and reduces the risk of human error.
Digitalised quality control around the injection molding cell allows us to define maximum defect quantities, tolerance limits, and accepted size ranges.
Key elements of an automated injection molding cell
Although every product and project is different, most automated injection molding cells at Mikropakk are built from similar building blocks.
Automated material supply
Raw material handling is automated to reduce manual work and maintain a clean production environment. Granulate is transported via closed vacuum systems to central dryers and then to the injection molding machines in the right quantity and condition. Operators only need to refill the material source, not load each machine individually.
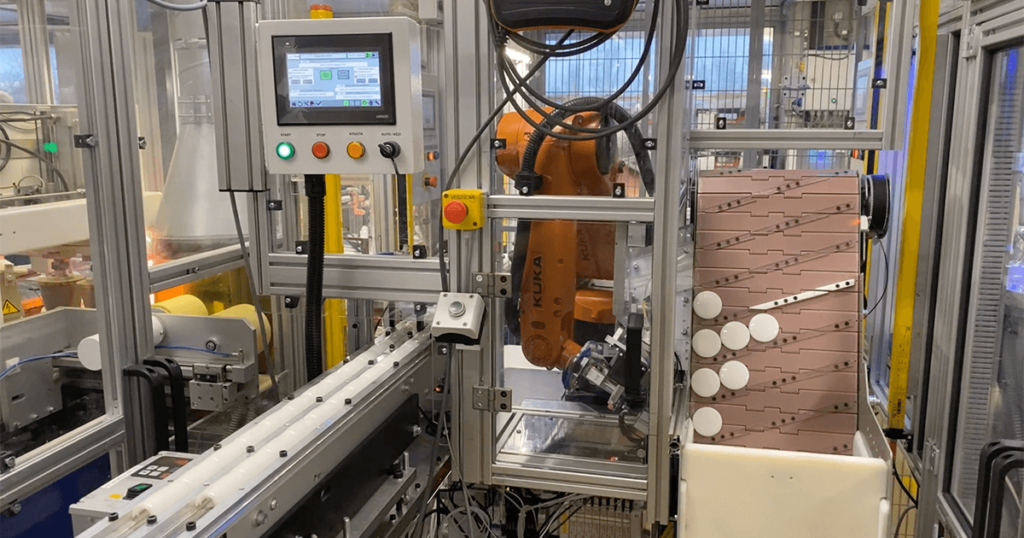
Robotised part take-out and handling
Above or next to the machines, multi-axis industrial robots remove parts from the mold and place them on conveyors, rotary tables, or pallets. This stabilises cycle times, protects delicate parts, and ensures that components always arrive at downstream stations in a predictable position and orientation.
Inline assembly and decoration
Depending on the product, several operations can be integrated directly after molding, such as:
- inserting and fixing additional components
- ultrasonic welding or other joining technologies
- plasma surface treatment to improve adhesion
- pad printing or other decoration processes
By connecting these operations into one automated cell, we reduce separate handling steps and keep the entire process under controlled conditions.
Automated quality control and data collection
Inline quality assurance is a key part of our automation projects. Camera systems and other sensors check presence, position, dimensions, colours, decoration quality, and functional behaviour. Results are evaluated automatically; non-conforming parts are removed from the flow and stored separately.
Measurement and test data are logged during production and linked to batches. This makes them traceable for customers and for our own engineers, and supports both audits and future optimisation.
Injection molding automation in practice
A good example of injection molding automation in practice is the production line for the applicator of the Lenzetto Spray medical device.
- A vibrating feeder loads, sorts, and orients the main plastic components.
- The parts move onto a rotating table where each element is assembled in sequence.
- Ultrasonic welding creates the final joint.
- A functional check verifies that the assembly works as intended.
- Plasma surface treatment activates the closed plastic surface and improves paint adhesion.
- The applicator goes through a one- or multi-stage pad printing process.
- A camera system monitors print quality, checks alignment, and removes misprinted parts.
- Production and test data are tracked continuously to catch deviations early and maintain stable output.
- Finished applicators are automatically collected, while defective parts are sorted and documented.
Watch our video about automated production:
Why injection molding automation is worth it
Industry 4.0 projects clearly show that automated injection molding cells can significantly increase output and enable stable 24/7 production without increasing headcount in the same proportion.
Reducing manual intervention lowers the risk of handling damage and assembly errors. Once the cell is properly set up and validated, precise machine and robot programming ensures consistently high quality even at high output.
For both semi-finished and finished products, we conduct:
- pressure tests,
- fit checks and
- functionality tests.
Test results are stored and linked to production batches, making them traceable for customers and for our own engineers. This level of documentation supports root cause analysis, audits, and continuous improvement projects.
Safety also improves with automation. Enclosed-cell robots and appropriate guarding separate people from moving equipment, while still allowing operators and maintenance staff to access the cell safely when needed.
Automated injection molding lines tailored to your product
No products or business cases are exactly the same. That is why our automation solutions for injection molding are always tailored to the specific component, volume, and quality requirements.
Depending on the project, we design:
- fully in-line automated cells that integrate molding, assembly, decoration, and quality control
- off-line or out-of-line automation that receives molded parts from several machines
- hybrid solutions that combine automated and manual steps where that makes most sense
With years of experience and a focus on our clients’ needs, we provide both in-line and off-line automation solutions. We customize each automation project to meet our customers’ unique requirements, using high-quality KUKA robots and other advanced technologies.
One of our successful projects involved manufacturing 4 million units per year of the Lenzetto Spray medical device applicator. With our advanced technology, this number can increase to 5 million. Despite the high volume, we maintained top quality through continuous data monitoring.
We are ready to automate the manufacturing of your product. Contact us, and our team will gladly provide you with more details!
